The United States is often hailed as a country of immigrants, but in reality there are complex social and cultural factors which play a role in the U.S. immigrant experience, one of the greatest being language. While the U.S. has no official language, English is the predominant means of communication, and plays a large role in multi-generational communications of immigrant communities. Our research seeks to answer: how does code-switching between English and native languages influence identity formation and social interactions among different generations within immigrant communities? Through participant observation and interviews at Los Angeles Latino and Chinese American church communities, we found that first-generation immigrants code-switch more often in work and public environments, whereas second-generation immigrants code-switch for the sake of multi-generation communication. Overall, we demonstrate that through code-switching, immigrant families and subsequent generations struggle to balance assimilation into American culture and the ability to preserve their cultural identity.
Introduction and Background
According to Pew Research (2020), “more than 1 million immigrants arrive in the U.S. each year.” With the arrival of various ethnic groups to the United States, and integrating themselves into American culture, new cultural exchanges emerge. Nevertheless, discrimination against migrants persists, hindering their integration and sense of belonging. Consequently, migrants often assimilate into the dominant hegemonic groups’ culture – rejecting their own.
Because of the ongoing presence of discrimination, it is crucial to understand the impact of dominant ideologies on both first-generation migrant communities and subsequent generations.
Language plays a key role in identity formation, with immigrants often teaching their children their native languages to maintain cultural ties. However, pressures to adapt to the dominant culture often lead parents to prioritize English as a first language. So how does learning your native language influence your identity and that of your children amidst a society that prioritizes English as the official language? Multiple studies have focused on code-switching as a form of expressing cultural identity (Bosire 2006). According to Myers-Scotton (1993), code-switching is defined as the mixing of different codes (or languages) by speakers in the same conversation (video explanation on code-switching). Moreover, scholars have also highlighted code-switching as a form of learning (Kremin et al. 2022) and socializing (Wei 1995; Lee 2019). Yet, Rangel et al. (2015) have critically emphasized the amount of stigmatization code-switching continues to receive. For this reason, our research focused on code-switching among immigrant communities in the United States, particularly focusing on the contrasts and similarities between first-generation and subsequent generations of immigrants. This study contributes to the wider discussion of code-switching as we explain from a sociolinguistic perspective how migrants and subsequent generations express their identity in a country where non-standard languages are viewed as inferior to standard English. Through qualitative methods, this research answers the following questions: how does code-switching between English and native languages influence identity formation and social interactions among different generations within immigrant communities? Our findings show that through code-switching, immigrant families and subsequent generations struggle to balance assimilation into American culture and the ability to preserve their cultural identity.
Methods
We collected data from two different churches in the Los Angeles area, with participants from Chinese and Latino/a descent communities. We used both participant-observation and semi-structured interview methods. The former was to note how speakers interacted in public spaces, specifically those that are similar in purpose. The latter was to hear the opinions of our participants about their language use.
Our observations took place in group settings, during which we took notes on verbal and non-verbal interactions between three groups: first-generation, second-generation, and a mixed group of both. We chose to limit the time of our observations to 15-25 minutes (due to assignment and situational constraints). In interviews, we spoke to two first-generation parents from each ethnic demographic (Latino or Chinese), ranging from middle-aged to older adults, and with one of each of their (second-generation) children, ranging from young to regular adults.
After data collection, we first compared answers within the most specific group, for example, responses from first-generation Latinos or from second-generation Chinese Americans. Then, we compared the data between generations within the same immigrant group (e.g. responses from Latinos), and the same generation between immigrant groups (e.g. second-generation responses). These were chosen as the methods for analysis because they forced us to consider all possible nuances between the various groups and once we had data for a set of the smaller groups (same generation & ethnicity) we could accurately compare the data for the larger groups (ethnic vs generational).
Results
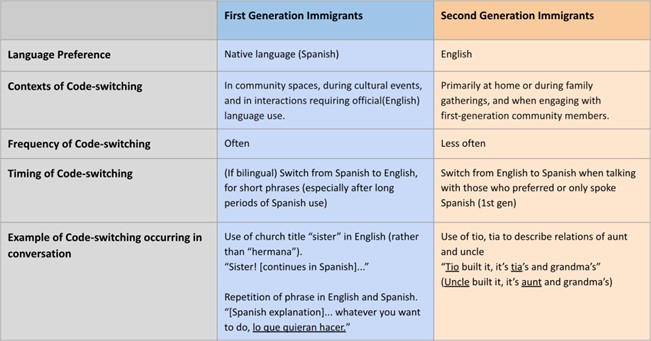
The table illustrates the comparison between first-generation immigrants and second-generation immigrants. We observed various factors of code-switching between both generations and discovered that there is a major difference in the context of code-switching. First-gen has been found to code-switch more often and will code-switch in the context of their root community’s events or situations that require using English. On the other hand, second-gen has been found to code-switch less in general. Code-switching behavior only occurs when they are speaking to people whose first choice of language is Spanish or native Spanish speakers.
Discussion and Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings touch on the importance of language use and perspectives from the first and second generations, particularly with an emphasis on the role played by code-switching among the groups. This research seeks to delve into the effect that code-switching brings in the process of identity formation and socialization of immigrant families and the generations. Therefore, it looks deeper into individual experiences and perspectives to understand the complex position this language takes in this domain. However, language behaviors observed among first and second-generation immigrants more than confirm that code-switching is the most effective tool through which to fully understand the subtleties of bilingualism and acculturation.
First-generation immigrants are struggling to learn and use English in respect to their native languages, and this shows a conscious choice to balance between assimilation and retention of culture. This has been seen in situations where some people never saw English as very important compared to their mother tongue; and that has also seemed to be the area of difficulty in integration, but to them, it’s an area of great importance. For code-switching of second-generation immigrants, it shows some ways that language influences identity and integration with society. These show movement away from an identification with American culture and toward the linguistic assimilation of their parent-native languages. Others maintain strong ties to their cultural heritage by being bilingual. They illustrate perfectly how family and personal language attitudes condition one’s approach to code-switching as a means of bicultural identity navigation. This approach further infiltrates the appreciation of code-switching as a changing and context-bound practice that reflects the challenges and opportunities presented to immigrant communities in maintaining their linguistic heritage in another environment. In this dimension, it calls for comprehensive recognition of multifarious language roles within the experience of migration. We also must observe the aspect of functionality and symbolism, and ultimately, consider the wider implications for the number of cultural identity, social integration, and intergenerational shifts.
While the researchers question the negative stamp of code-switching and non-standard language use, rather, it encourages a broader acceptance of bilingualism, or on a higher level, even of multilingualism, that respects the differences in the use of languages. This work was undertaken in order to remove the stigma from practicing code-switching, keeping in view the positive aspects of bilingualism, which pertains to strengthened cultural ties and increased flexibility of personalities. Overall, our research offers new and interesting data, bringing relevant insights and contributions to research in sociolinguistics on code-switching among immigrants. Through empirical evidence we have shown how practices of identity, cultural preservation, and adaptation intertwine with language practices. This highlights how complex the nature of language used among immigrant communities is and does provide a window into socio-cultural forces which are at play on code-switching and bilingualism. This serves to open further investigations into the complexity of the relations between language, identity, and community in diverse sociolinguistic contexts.
References
Bosire, M. (2006). Immigrant Identity: Code Switching among Kenyans in Upstate New York. In Selected Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference on African Linguistics, ed. John Mugane et al., 44-52. Somerville, MA: Cascadilla Proceedings Project.
Budiman, A. (2020, August 20). Key findings about U.S. immigrants. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2020/08/20/key-findings-about-u-s-immigrants/.
Cher. L. L., (2019). Filling gaps or code choice? Code-switching across generations in colloquial Singapore Mandarin. Global Chinese 2019; 5(1): 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1515/glochi-2019-0001
Kremin, L. V., Alves, J., Orena, A. J., Polka, L., & Byers-Heinlein, K. (2022). Code-switching in parents’ everyday speech to bilingual infants. Journal of Child Language, 49(4), 714–740. doi:10.1017/S0305000921000118
Rangel, Natalie., Loureiro-Rodriguez, Veronica., & Moyona, Maria Irene. (2015). “Is that what I sound like when I speak?”: Attitudes towards Spanish, English, and code-switching in two Texas border towns. Spanish in Context, 12(2), 177-198. https://doi.org/10.1075/sic.12.2.01ran
Wei, Li. (1995). Code‐switching, preference marking and politeness in bilingual cross‐generational talk: Examples from a Chinese community in Britain. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development,16(3), 197-214, https://doi.org/10.1080/01434632.1995.9994600